Drilling techniques
As a specialized drilling and sampling service provider, we offer a wide range of drilling techniques to cater to diverse geological formations and drilling requirements. Our drilling services include both manual and mechanical drilling, and we have extensive experience in working with various geological formations.
Our team of experts evaluates the problem, geology, and location to determine the best drilling technique for each project. We carefully consider factors such as the depth and diameter of the borehole, the required sampling method, and the soil or rock type to ensure that we use the most appropriate technique to obtain accurate and reliable results.
Our drilling services are tailored to meet the specific needs of each client, and we work closely with them throughout the entire process to ensure their satisfaction. Whether it is for environmental or geotechnical research, our goal is to provide the highest quality drilling services that meet the highest industry standards.

ROTOSONIC DRILLING
Sonic drilling is a highly advanced drilling technique that utilizes high-frequency resonance energy generated in the Sonic drill head by two rotating weights and transmitted along the drill pipe to the bit. Unlike other drilling techniques, sonic drilling rotates the drill bit at the same time, so that the resonance energy is evenly distributed between the bit and the material to be drilled. This allows us to drill almost all formations, from clay, gravel, and sand to rock, with maximum efficiency and productivity.
At Sialtech and Geosonic France, we use sonic drilling to obtain high-quality and mixed geology samples, with minimal excess drilling material released. The technique is ideal for both environmental and geotechnical research applications. In addition, we also use sonic drilling to install sampling tubes, as with other pressure- and impact-based drilling methods. Overall, sonic drilling is a cutting-edge technology that enables us to conduct drilling operations with unparalleled precision and accuracy.
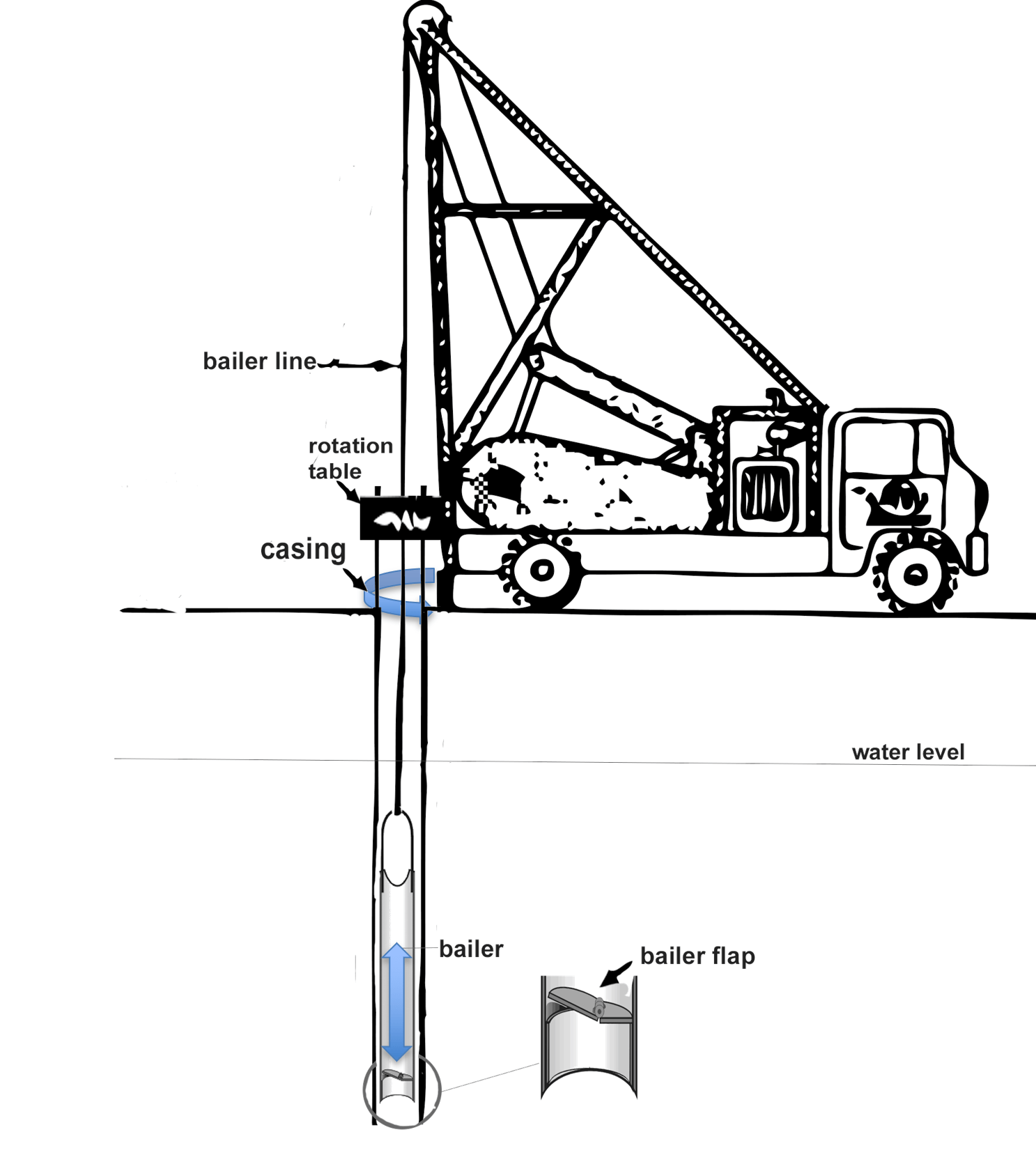
PERCUSSION (BAILER) DRILLING
Bailer drilling is a technique that involves using a pipe with a cutting edge at the bottom and a horizontal valve just above it to collect loose material. As the pipe is moved up and down, the loose material is collected in the bailer. The valve mechanism ensures that the drilled material does not fall back into the borehole when the bailer is raised. This technique is typically used below the groundwater level, and as such, we use an agave drill for pre-drilling.
Our team can carry out bailer drilling to depths of more than 50 metres, with a maximum diameter of 324 mm. Although the soil samples collected through bailer drilling are typically very disturbed, they can still be used for profile tracing in homogeneous soils. In very heterogeneous soils, the profile tracing may be less reliable. While the strongly disturbed samples from the bailer are usually not suitable for sampling, we can use a coring apparatus to take an undisturbed sample at the desired depth after removal of the bailer. Our bailer drilling is carefully conducted, and we take great care to ensure that the sampling tubes and seals are applied accurately.
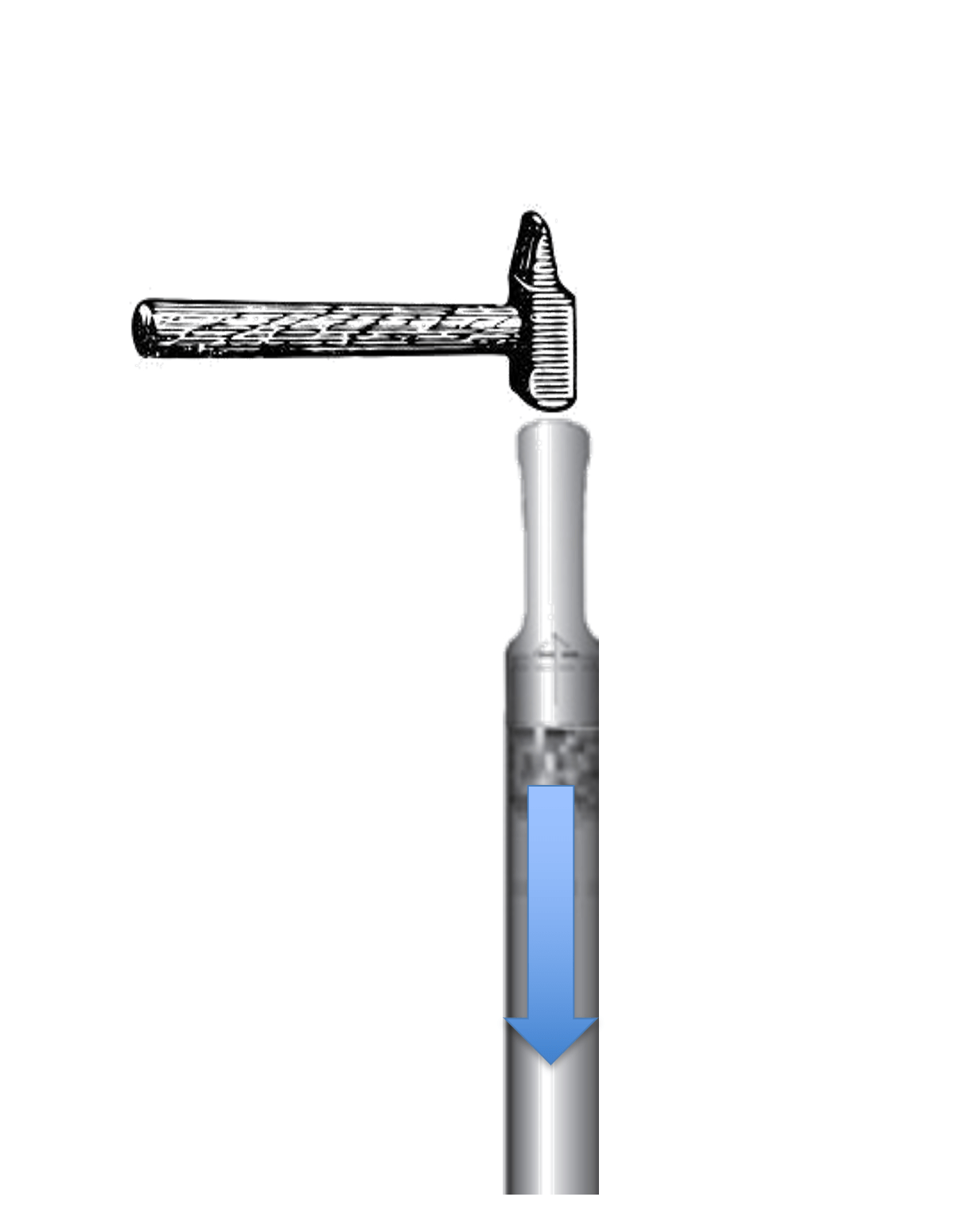

DIRECT-PUSH AND HAMMER DRILLING
The direct-push and hammer drilling technique is an effective method for obtaining undisturbed soil samples at any desired depth without washing or dilution. The technique involves the use of a cylindrical drill with a cutting edge that is either pressed or hammered into the soil, with the samples collected through the use of an inner tube and a plastic tube.
At Sialtech and Geosonic France, we utilize both manual and mechanical equipment to carry out direct-push and hammer drilling, including percussion coring tubes. Depending on the drilling method used, we can achieve depths of up to 30 meters, with drill diameters ranging from 32 mm to 86 mm.
In addition to soil sampling, direct-push and hammer drilling techniques can also be used for the installation of sampling tubes. By using a removable or “lost” drive point to function as a casing, the filter can be installed at the correct depth with minimal soil disturbance and no excess soil material being released during drilling. This makes the technique ideal for a variety of environmental and geotechnical research applications.
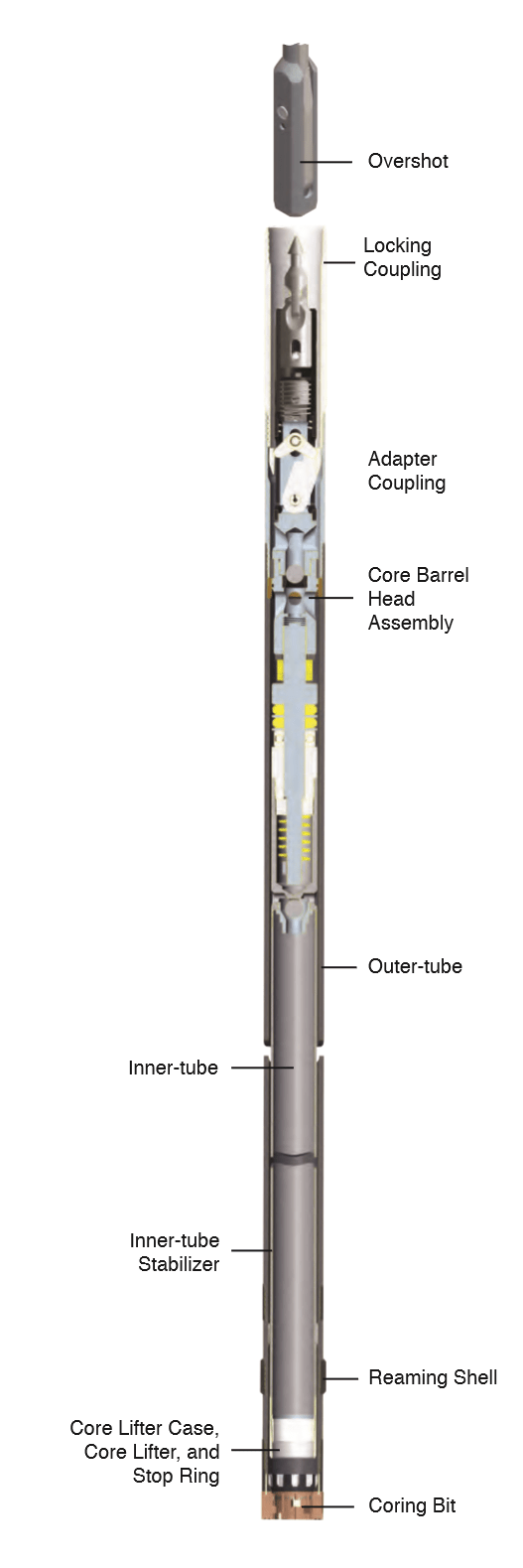
CORE DRILLING
Core drilling is a specialized drilling technique that involves using a rotating outer core barrel with a drill bit, along with a stationary inner core barrel. During the drilling process, water, mud fluid, or air is added to cool the drill bit and remove the bore dust. The drilling is done in equal steps of 1.5 meters (or a multiple thereof) to ensure accuracy and precision.
After each run, the inner core barrel is carefully extracted from the drill casing and emptied. The extracted core is then stored in a specially designed box for further analysis. Core drilling is typically used to penetrate through soil layers that are too hard for other drilling techniques, such as bailing, especially when drilling deeper.
At Geosonic France and Sialtech, we have years of experience in core drilling, and we use state-of-the-art equipment and technology to ensure that our core samples are of the highest quality. Our team of experts has the knowledge and expertise to handle even the most challenging drilling projects, and we work closely with our clients to ensure that their specific needs and requirements are met.
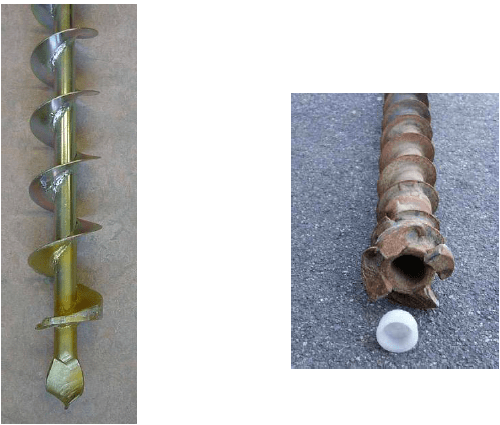

AUGER DRILLING
Auger drilling is a common drilling technique used for soil investigation and sampling. At Sialtech an Geosnic France, we offer auger drilling services with a maximum diameter of 320 mm, which is suitable for sampling soils with a lot of coarse material. The depth we can reach depends on the drilling rig, the base, and the diameter used.
There are three types of auger drilling: continuous flight auger, hollow auger, and cased auger. Continuous flight auger drilling uses a spiral that is rotated by a drill engine, and the drill screws itself into the soil. The drill is lengthened by using an extension piece until the desired depth is reached, and then the soil is pulled up with the drill. This technique is suitable for taking soil samples for environmental and archaeological site investigations and for tracing profiles.
Hollow auger drilling uses a spiral drill with a hollow inner pipe that is closed off at the bottom with a lockable lid. We take a sample at the reached depth with the help of a ram cutter or a cutting box, and we can optionally install a sampling tube through the hollow auger. However, since the hollow auger raises a large quantity of soil material during drilling, this method is not suitable for tracing profiles.
Finally, cased auger drilling is a technique in which the continuous flight auger drills through a casing that is lowered at the same time as the auger. This technique is used to drill through a contaminated soil stratum and when percussion drilling is not possible, such as in the case of clay soils and soils above groundwater level.
